This is how you can help save the lives of three other people
Today, 14 June, is World Blood Donor Day. Half of the population will, at some point in their life, depend on a blood transfusion
Patricia Cabezuelo
Wednesday, 14 June 2023, 10:52
One in two people in Spain will need extra blood at some point in their lives. This means that half of the population will be dependent on a transfusion at some point in time.
Traffic accidents, childbirth, transplants and surgeries of all kinds are just some of the situations in which we or one of our loved ones may find ourselves. And in all of them it is crucial that there is enough blood to cover the needs.

Every 3 seconds
someone needs blood
1 in 10
people admitted to a
hospital requires a transfusion
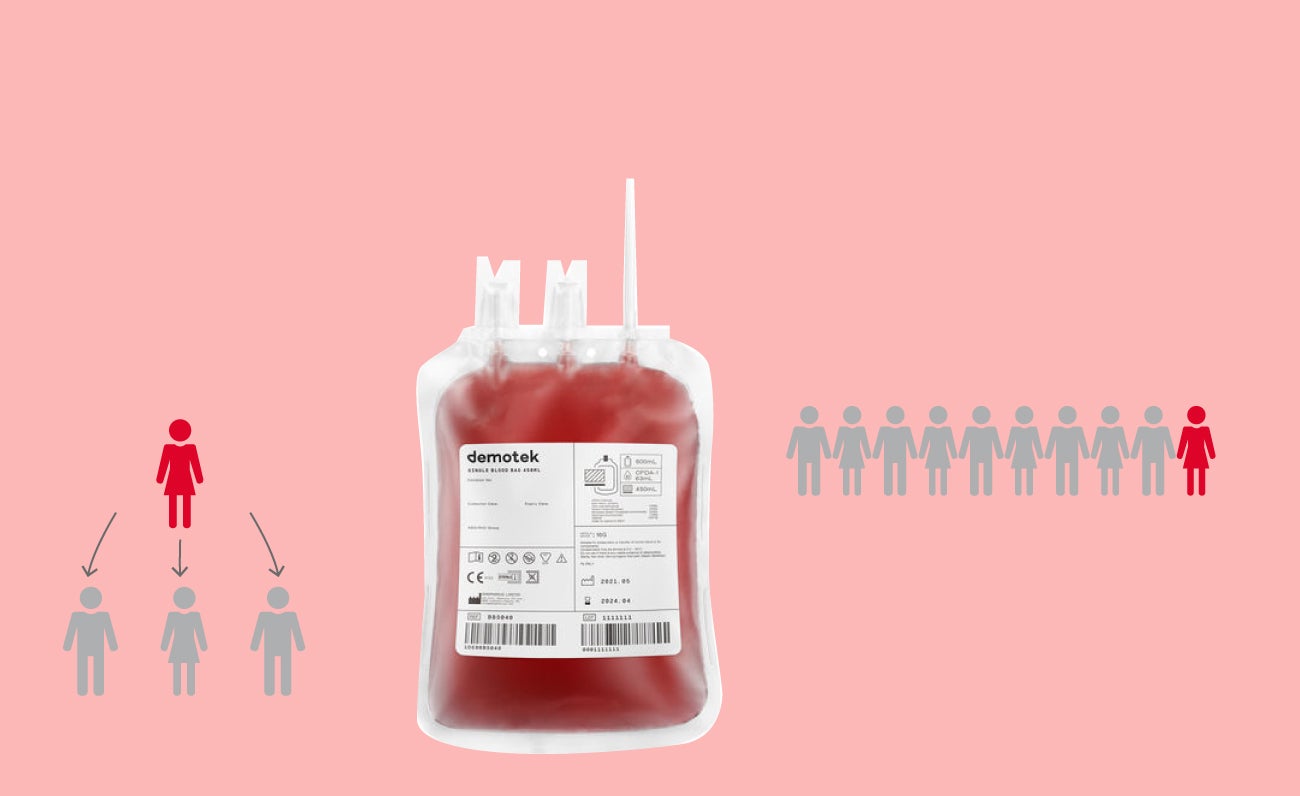
A donation of
450 ml
of blood can
save 3 lives

Every 3 seconds
someone needs blood
1 in 10
people admitted to a
hospital requires a transfusion
A donation of
450 ml
of blood can
save 3 lives

Every 3 seconds
someone needs blood
A donation of
450 ml
of blood can
save 3 lives
1 in 10
people admitted to a
hospital requires a transfusion

Every 3 seconds
someone needs blood
A donation of
450 ml
of blood can
save 3 lives
1 in 10
people admitted to a
hospital requires a transfusion
"In Spain, as in the rest of Europe, donation is an altruistic and voluntary act," explained Cristina Arbona, director of the Valencia region blood transfusion centre. "At the moment we are self-sufficient and do not need to depend on other countries, such as the United States, where donation is paid for and some have it as a means of subsistence, with all that this entails."
Here we are going to look more deeply into the donation process, how blood is obtained, what it is used for and how a transfusion centre works.
People with blood group O negative (O-) are the so-called universal donors because they are compatible with everyone, but transfusion centres insist: "All groups are necessary. If we have a B+ patient, the best thing to do is to give them their own group: B+."
In Spain, the majority of the population has 0+ and A+, so they are the most likely to have reserves of their blood group, while the minority groups are the most likely to require donations.
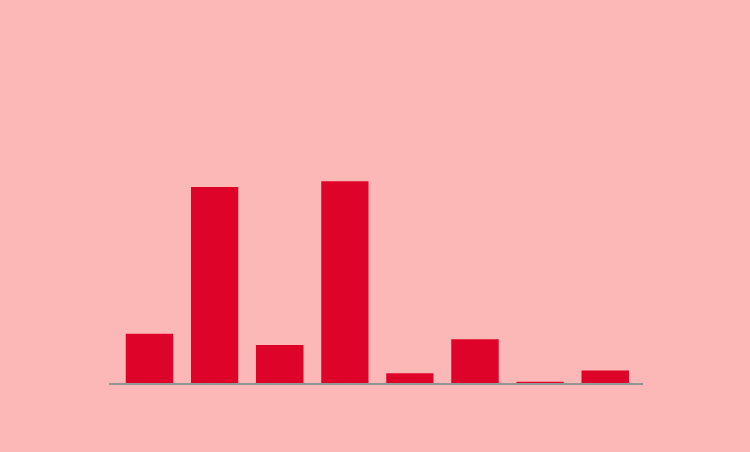
Distribution of blood groups in Spain
%
36,0
35,0
9,0
8,0
7,0
2,5
2,0
0,5
A+
O-
O+
A-
B-
B+
AB-
AB+
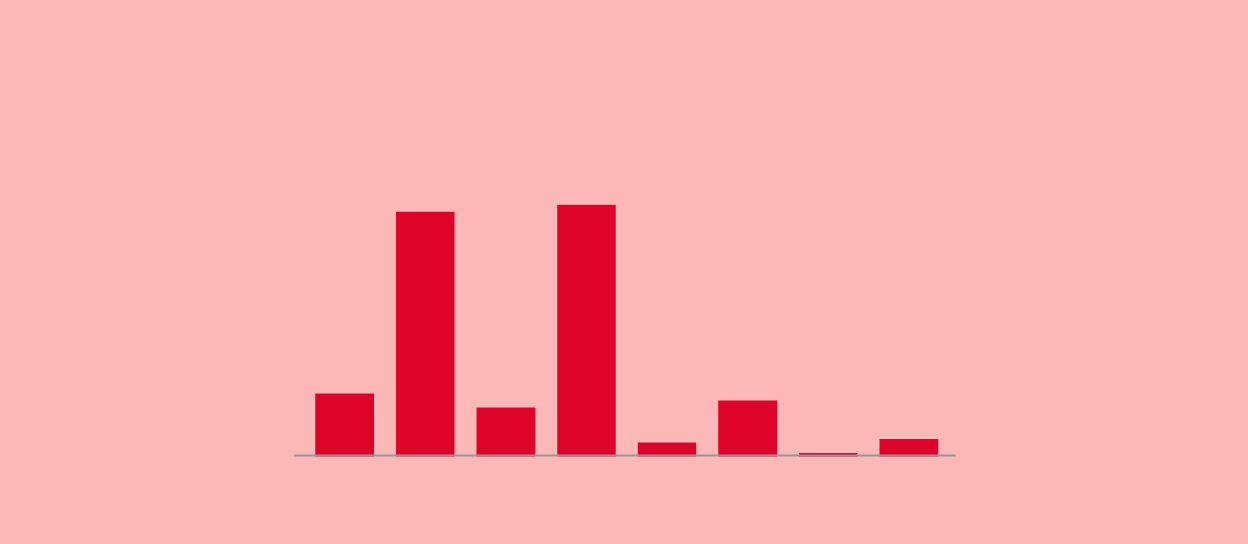
Distribution of blood groups in Spain
%
36,0
35,0
9,0
8,0
7,0
2,0
2,5
0,5
A+
O-
O+
A-
B-
B+
AB-
AB+

Distribution of blood groups in Spain
%
36,0
35,0
8,0
9,0
7,0
2,5
2,0
0,5
A+
O-
O+
A-
B-
B+
AB-
AB+
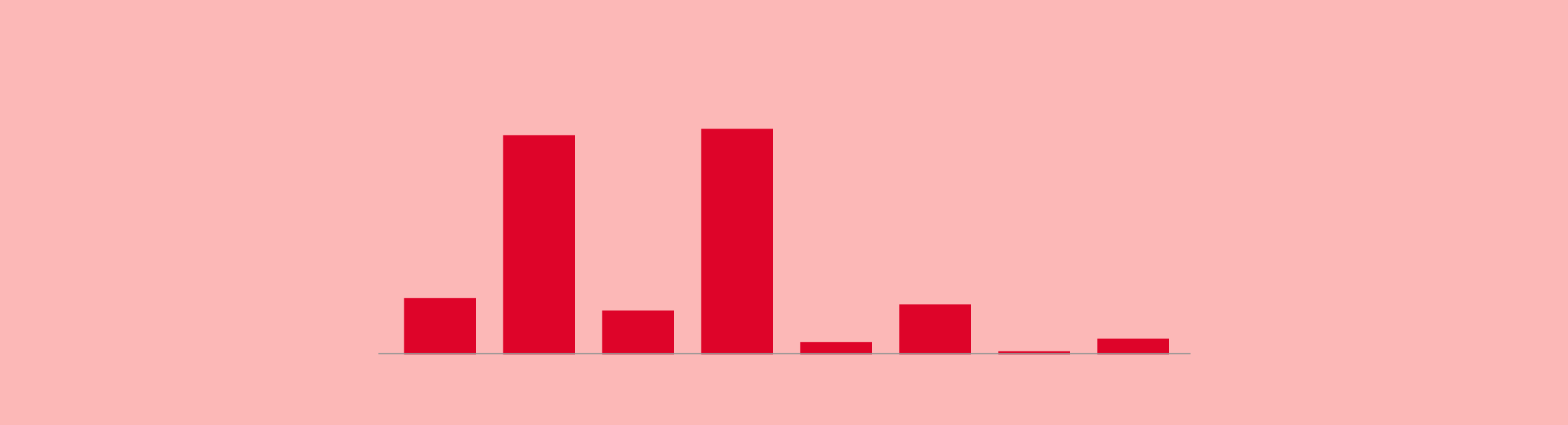
Distribution of blood groups in Spain
%
36,0
35,0
8,0
9,0
7,0
2,5
2,0
0,5
A+
O-
O+
A-
B-
B+
AB-
AB+
Whatever your blood type, blood has the same essential components and all of them are used to save lives.
Components of blood
Sangre centrifugada:
55%
Plasma
Proteínas
7%
albúmina, 57%; globulinas, 38%;
fibrinógeno, 4%; protrombina, 1%
Agua
91%
Otros solutos
2%
nutrientes, desechos, iones, gases,
sustancias reguladoras
45%
Elementos formes
Glóbulos rojos
98%
eritrocitos ó hematíes
Góbulos blancos
1%
leucocitos
Plaquetas
1%
trombocitos
Components of blood
Sangre centrifugada:
55%
Plasma
Proteínas
7%
albúmina, 57%; globulinas, 38%;
fibrinógeno, 4%; protrombina, 1%
Agua
91%
Otros solutos
2%
nutrientes, desechos, iones, gases,
sustancias reguladoras
45%
Elementos formes
Glóbulos rojos
98%
eritrocitos ó hematíes
Góbulos blancos
1%
leucocitos
Plaquetas
1%
trombocitos

Components of blood
Sangre centrifugada:
55%
Plasma
7%
91%
2%
albúmina, 57%; globulinas, 38%;
fibrinógeno, 4%; protrombina, 1%
Proteínas
Agua
Otros solutos
nutrientes, desechos, iones, gases,sustancias reguladoras
45%
Elementos formes
Glóbulos rojos
Góbulos blancos
Plaquetas
eritrocitos ó hematíes
leucocitos
trombocitos
98%
1%
1%
Components of blood
Sangre centrifugada:
55%
Plasma
albúmina, 57%; globulinas, 38%;
fibrinógeno, 4%; protrombina, 1%
Proteínas
Agua
Otros solutos
7%
91%
2%
nutrientes, desechos, iones, gases,sustancias reguladoras
45%
Elementos formes
Glóbulos rojos
Góbulos blancos
Plaquetas
eritrocitos ó hematíes
leucocitos
trombocitos
98%
1%
1%
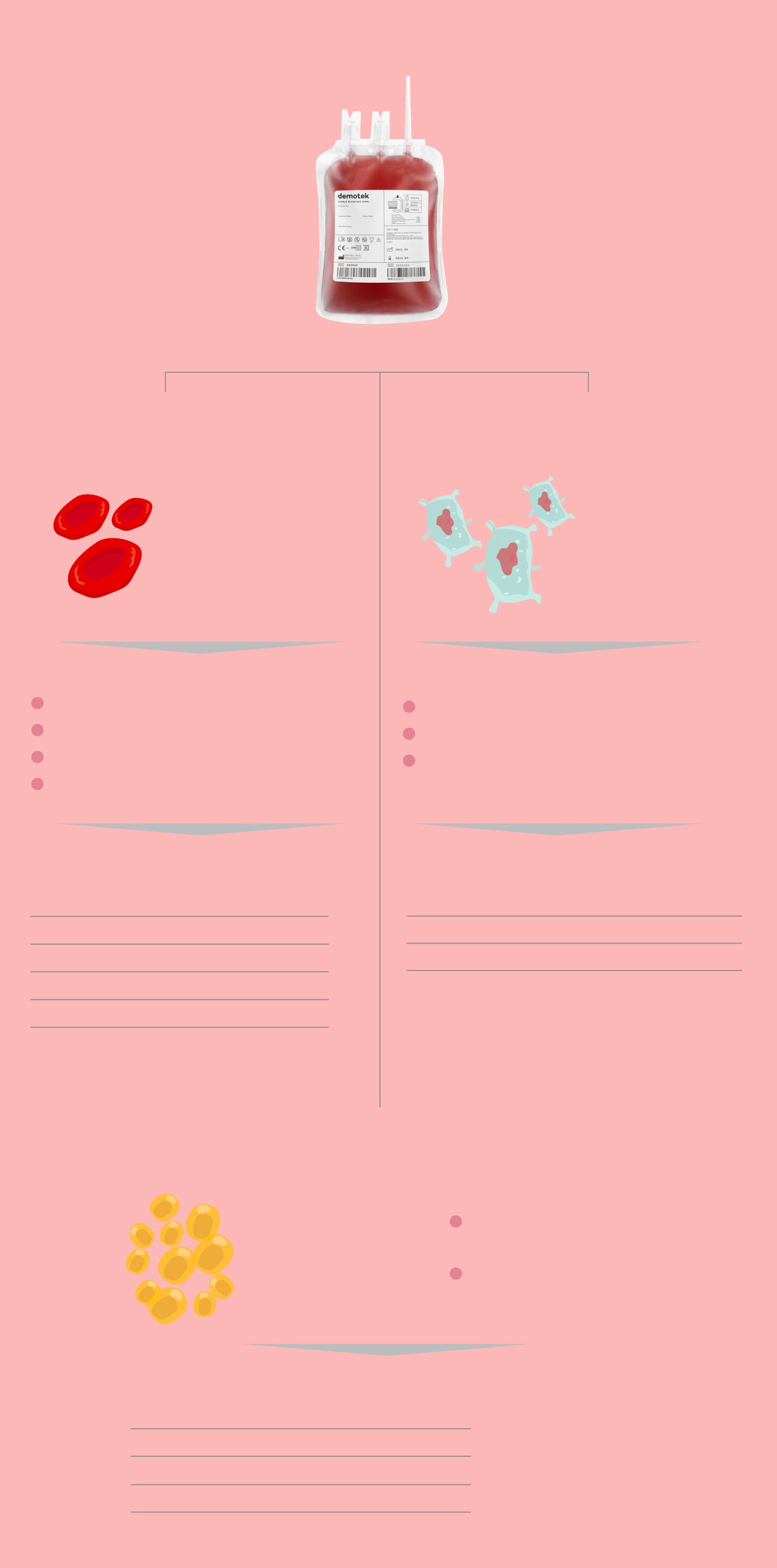
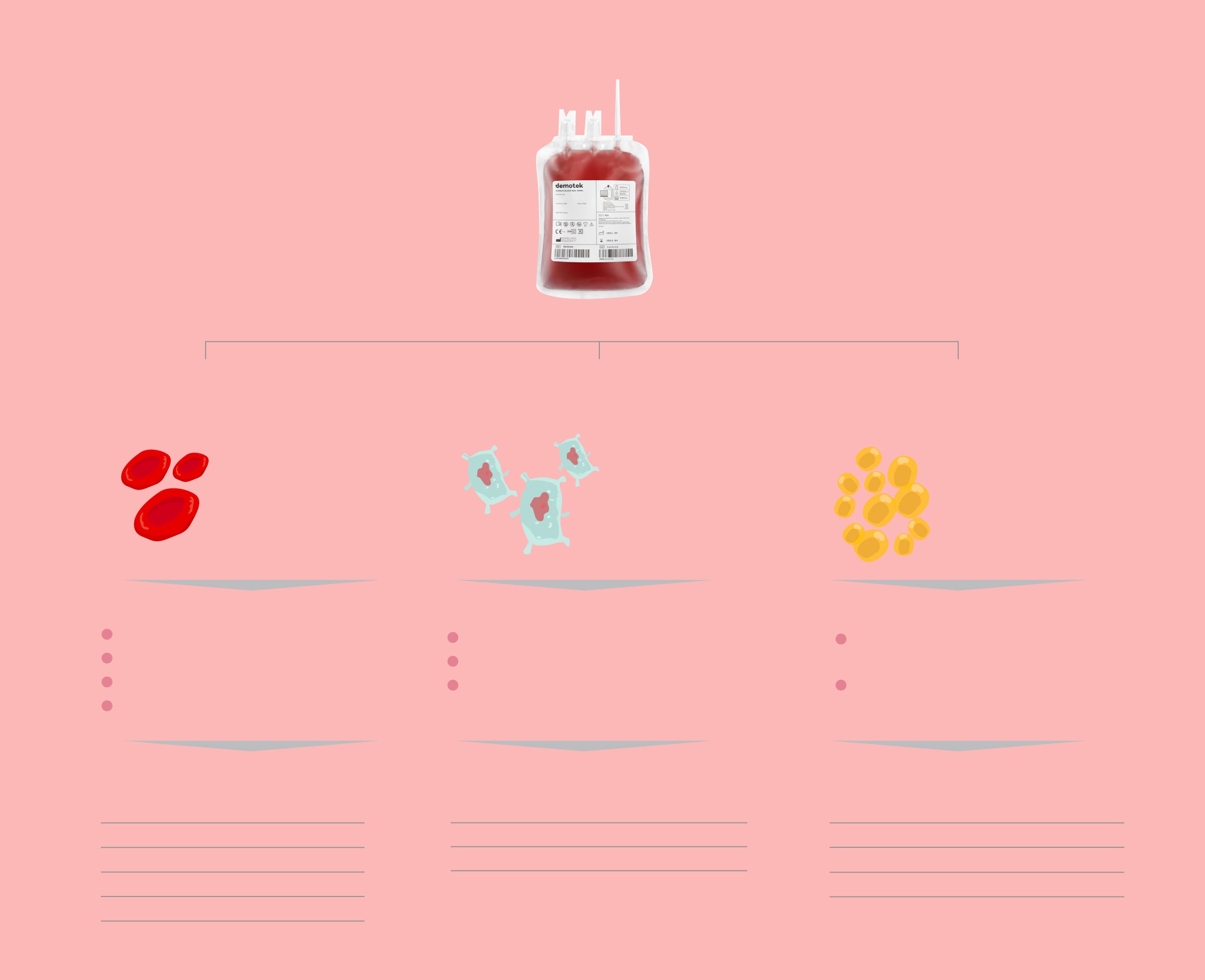
There are two types of donations, traditional and apheresis. In traditional donation, 450 ml of blood is collected from the donor and divided in the laboratory into red blood cell concentrate, plasma and platelets. Each of these components has different conditions and conservation needs. In addition, each has a different use.

From 1 donation of
450 ml
you can extract
Concentrado de glóbulos rojos
Llevan el oxígeno de los pulmones a todo el organismo y lo mantienen vivo
CONSERVACIÓN
2 a 6ºC
DURACIÓN
42 días
PACIENTES CON
Anemia crónica cirrosis
Quimioterapia
Pérdidas crónicas
Grandes hemorragias partos, accidentes
de tráfico, cirugías complicadas, etc
CUÁNTA SE USA
Unidades
6-8
OPERACIÓN DE CADERA
PARTO COMPLICADO
4-6
ACCIDENTE DE TRÁFICO
20-30
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
20
30
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
50
TRASPLANTE DE MÉDULA
Plaquetas
Las primeras células que hacen tapón ante una hemorragia y evitan que se sangre espontáneamente
CONSERVACIÓN
Temperatura
ambiente
DURACIÓN
5-7 días
PACIENTES CON
Para trasfundir una unidad de plaquetas a un paciente se necesitan 4 o 5 donaciones
Sepsis graves
Leucemia
Hemorragias masivas
CUÁNTA SE USA
Unidades
hasta 20
ENFERMOS DE LEUCEMIA
20
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
100
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
200
TRASPLANTE DE MÉDULA
Plasma
Es agua fundamentalmente con proteínas que tienen muchas funciones
CONSERVACIÓN
-30ºC
DURACIÓN
2-3 años
PACIENTES CON
Se usa poco transfundido, alrededor del 8% del que se extrae. Lo que se hace con el resto, te lo contamos más abajo
Alteraciones
de coagulación
Cirugías
complicadas
CUÁNTA SE USA
Unidades
6-8
ENFERMOS DE HÍGADO
10-20
CIRUGÍAS COMPLICADAS
hasta 100
ENFERMEDADES RARAS
20
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
40
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO

From 1 donation of
450 ml
you can extract
Concentrado de glóbulos rojos
Llevan el oxígeno de los pulmones a todo el organismo y lo mantienen vivo
CONSERVACIÓN
2 a 6ºC
DURACIÓN
42 días
PACIENTES CON
Anemia crónica cirrosis
Quimioterapia
Pérdidas crónicas
Grandes hemorragias partos, accidentes
de tráfico, cirugías complicadas, etc
CUÁNTA SE USA
Unidades
6-8
OPERACIÓN DE CADERA
PARTO COMPLICADO
4-6
ACCIDENTE DE TRÁFICO
20-30
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
20
30
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
50
TRASPLANTE DE MÉDULA
Plaquetas
Las primeras células que hacen tapón ante una hemorragia y evitan que se sangre espontáneamente
CONSERVACIÓN
Temperatura
ambiente
DURACIÓN
5-7 días
PACIENTES CON
Para trasfundir una unidad de plaquetas a un paciente se necesitan 4 o 5 donaciones
Sepsis graves
Leucemia
Hemorragias masivas
CUÁNTA SE USA
Unidades
hasta 20
ENFERMOS DE LEUCEMIA
20
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
100
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
200
TRASPLANTE DE MÉDULA
Plasma
Es agua fundamentalmente con proteínas que tienen muchas funciones
CONSERVACIÓN
-30ºC
DURACIÓN
2-3 años
PACIENTES CON
Se usa poco transfundido, alrededor del 8% del que se extrae. Lo que se hace con el resto, te lo contamos más abajo
Alteraciones
de coagulación
Cirugías
complicadas
CUÁNTA SE USA
Unidades
6-8
ENFERMOS DE HÍGADO
10-20
CIRUGÍAS COMPLICADAS
hasta 100
ENFERMEDADES RARAS
20
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
40
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO

From 1 donation of
450 ml
you can extract
Concentrado de glóbulos rojos
Plaquetas
Llevan el oxígeno de los pulmones a todo el organismo y lo mantienen vivo
Las primeras células que hacen tapón ante una hemorragia y evitan que se sangre espontáneamente
CONSERVACIÓN
CONSERVACIÓN
2 a 6ºC
Temperatura
ambiente
DURACIÓN
DURACIÓN
42 días
5-7 días
PACIENTES CON
PACIENTES CON
Para trasfundir una unidad de plaquetas a un paciente se necesitan 4 o 5 donaciones
Anemia crónica cirrosis
Sepsis graves
Quimioterapia
Leucemia
Pérdidas crónicas
Hemorragias masivas
Grandes hemorragias partos, accidentes
de tráfico, cirugías complicadas, etc
CUÁNTA SE USA
CUÁNTA SE USA
Unidades
Unidades
6-8
hasta 20
OPERACIÓN DE CADERA
ENFERMOS DE LEUCEMIA
20
PARTO COMPLICADO
4-6
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
ACCIDENTE DE TRÁFICO
100
20-30
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
200
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
TRASPLANTE DE MÉDULA
20
30
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
50
TRASPLANTE DE MÉDULA
Plasma
Es agua fundamentalmente con proteínas que tienen muchas funciones
CONSERVACIÓN
PACIENTES CON
-30ºC
Alteraciones
de coagulación
Cirugías
complicadas
DURACIÓN
2-3 años
CUÁNTA SE USA
Unidades
Se usa poco transfundido, alrededor del 8% del que se extrae. Lo que se hace con el resto, te lo contamos más abajo
6-8
ENFERMOS DE HÍGADO
10-20
CIRUGÍAS COMPLICADAS
hasta 100
ENFERMEDADES RARAS
20
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
40
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
From 1 donation of
450 ml
you can extract
Concentrado de glóbulos rojos
Plaquetas
Plasma
Llevan el oxígeno de los pulmones a todo el organismo y lo mantienen vivo
Las primeras células que hacen tapón ante una hemorragia y evitan que se sangre espontáneamente
Es agua fundamentalmente con proteínas que tienen muchas funciones
CONSERVACIÓN
CONSERVACIÓN
CONSERVACIÓN
-30ºC
2 a 6ºC
Temperatura
ambiente
DURACIÓN
DURACIÓN
DURACIÓN
42 días
5-7 días
2-3 años
PACIENTES CON
PACIENTES CON
PACIENTES CON
Para trasfundir una unidad de plaquetas a un paciente se necesitan 4 o 5 donaciones
Se usa poco transfundido, alrededor del 8% del que se extrae. Lo que se hace con el resto, te lo contamos más abajo
Anemia crónica cirrosis
Sepsis graves
Alteraciones
de coagulación
Quimioterapia
Leucemia
Pérdidas crónicas
Cirugías
complicadas
Hemorragias masivas
Grandes hemorragias partos, accidentes
de tráfico, cirugías complicadas, etc
CUÁNTA SE USA
CUÁNTA SE USA
CUÁNTA SE USA
Unidades
Unidades
Unidades
6-8
hasta 20
6-8
OPERACIÓN DE CADERA
ENFERMOS DE HÍGADO
ENFERMOS DE LEUCEMIA
20
10-20
PARTO COMPLICADO
4-6
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
CIRUGÍAS COMPLICADAS
ACCIDENTE DE TRÁFICO
100
20-30
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
hasta 100
ENFERMEDADES RARAS
200
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
TRASPLANTE DE MÉDULA
20
20
TRASPLANTE DE CORAZÓN
30
40
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
TRASPLANTE DE HÍGADO
50
TRASPLANTE DE MÉDULA
Faced with so much demand, is there enough blood? This is exactly the function of the transfusion centres. The director of the one in the Valencia region explained: "Our fundamental mission is to guarantee the supply of blood components and other substances of human origin to the different hospitals to cover the needs of patients and, above all, to do so with the maximum guarantees of quality and safety. For years we have had a very constant and very fluid donation. We have managed to ensure that donation is considered a natural act and this has allowed us to make donors aware of this and to make continuous and constant donations," concluded Cristina Arbona.
The figures prove it. The number of blood donations in Spain exceeded 1.7 million in 2021. This means that pre-pandemic levels have been recovered, when there was a slight drop of 5% associated with the postponement of non-urgent hospital interventions. Stability now dominates: "The calculation of our needs is based on what we distribute, and the day that amount does not come in, it is subtracted from the stock, so the next day we put mechanisms in place so that a little more comes in," said Dr Arbona.
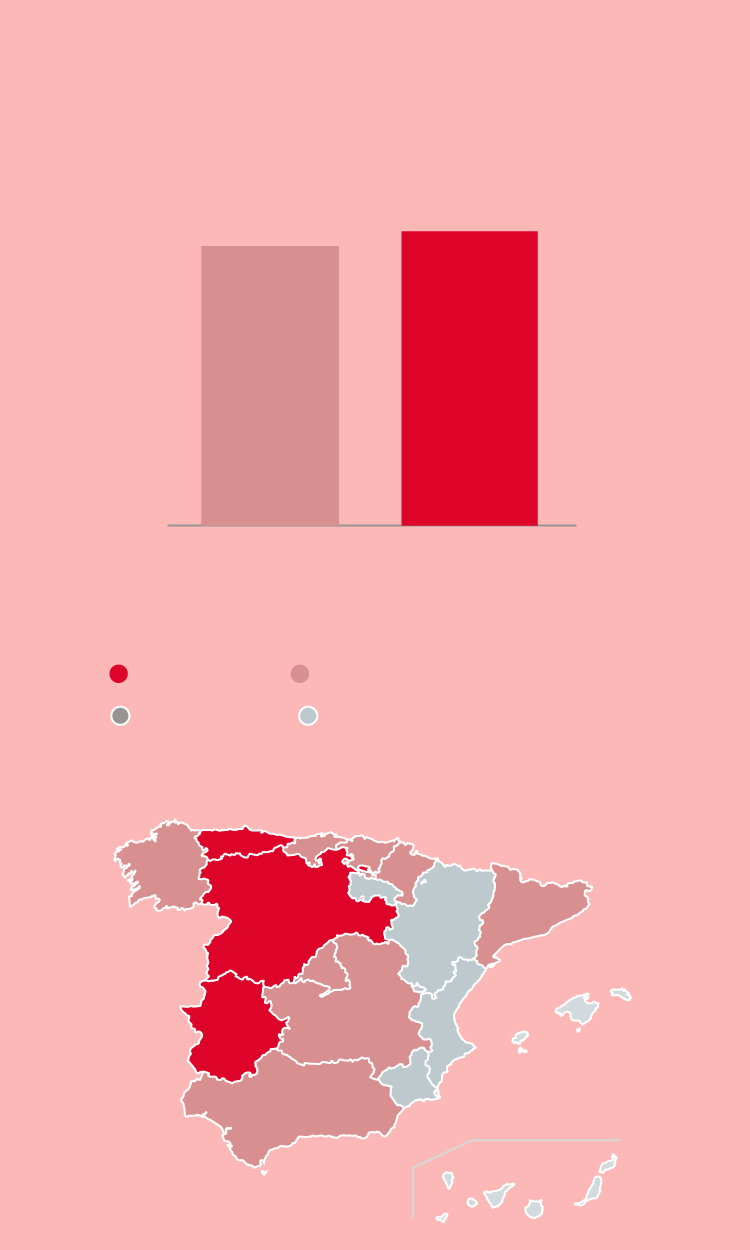
Evolution of donors
En España
1.720.402
1.632.447
2020
2021
Tasa por cada mil habitantes en 2021
Más de 40
De 35 a 40
De 30 a 34,9
Menos de 30
Asturias
40,56
Cast. y León
45,55
Extremadura
C. Valenciana
48,52
34,01
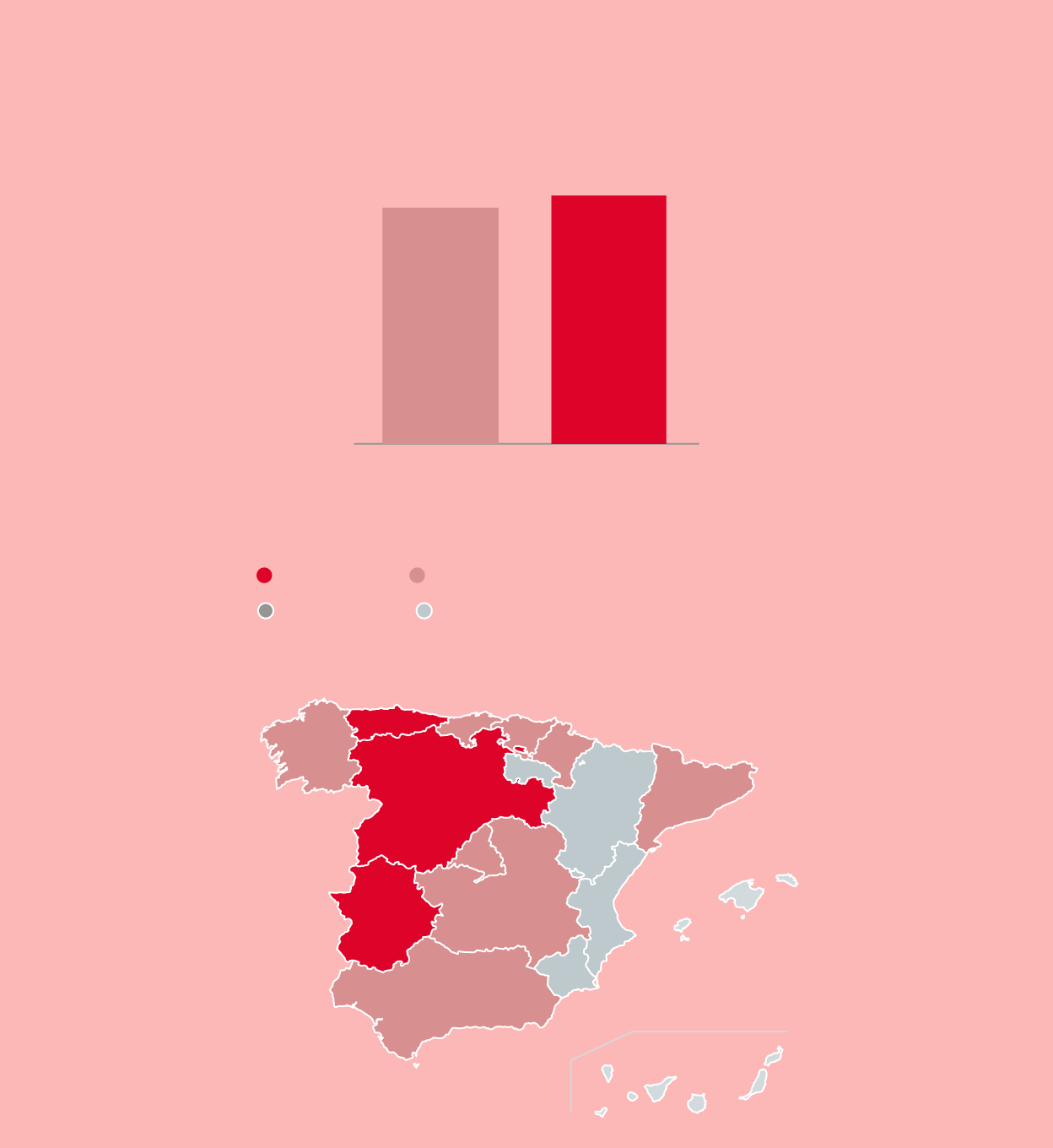
Evolution of donors
En España
1.720.402
1.632.447
2020
2021
Tasa por cada mil habitantes en 2021
Más de 40
De 35 a 40
De 30 a 34,9
Menos de 30
Asturias
40,56
Cast. y León
45,55
C. Valenciana
Extremadura
34,01
48,52
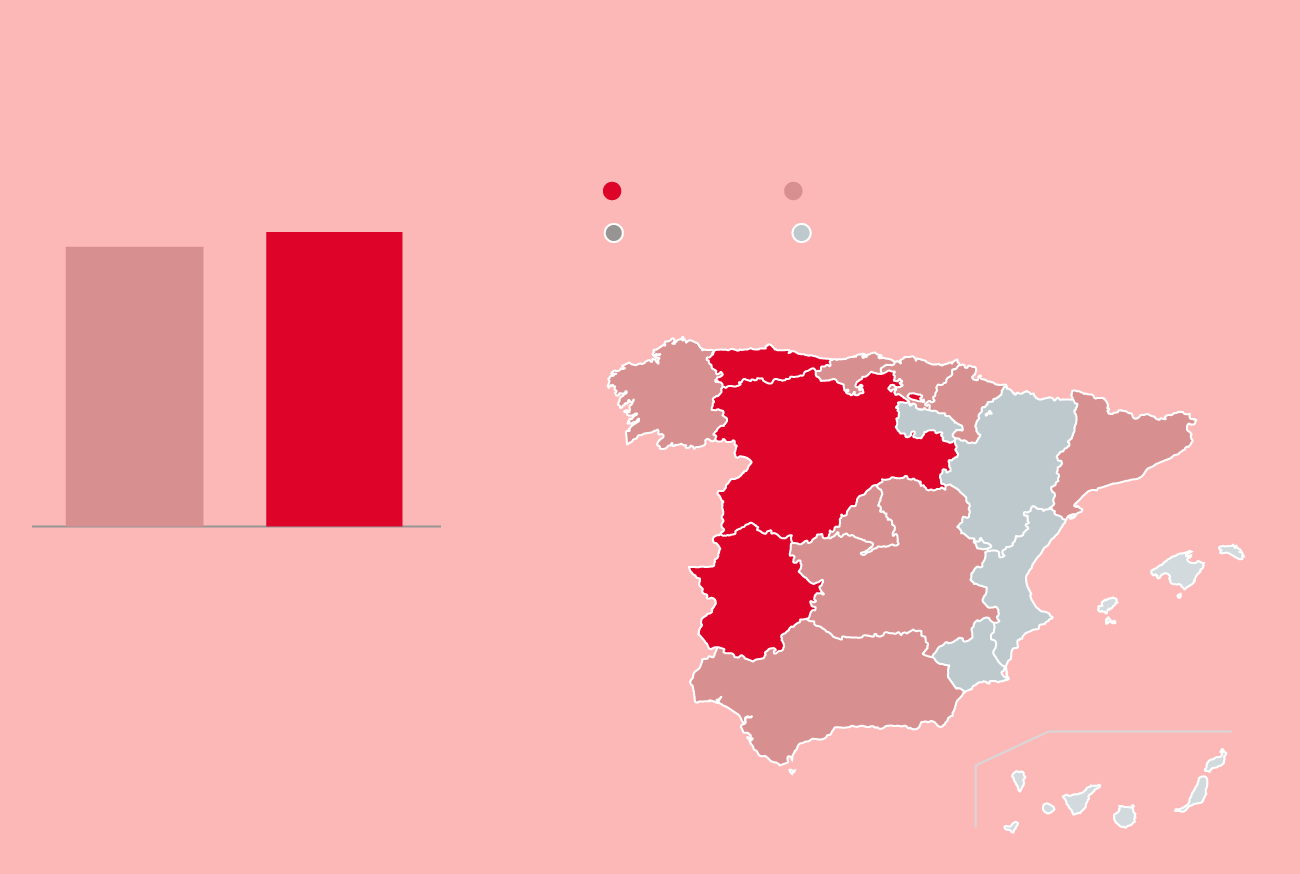
Evolution of donors
En España
Tasa por cada mil habitantes en 2021
1.720.402
Más de 40
De 35 a 40
1.632.447
De 30 a 34,9
Menos de 30
Asturias
40,56
Cast. y León
45,55
2020
2021
C. Valenciana
Extremadura
34,01
48,52
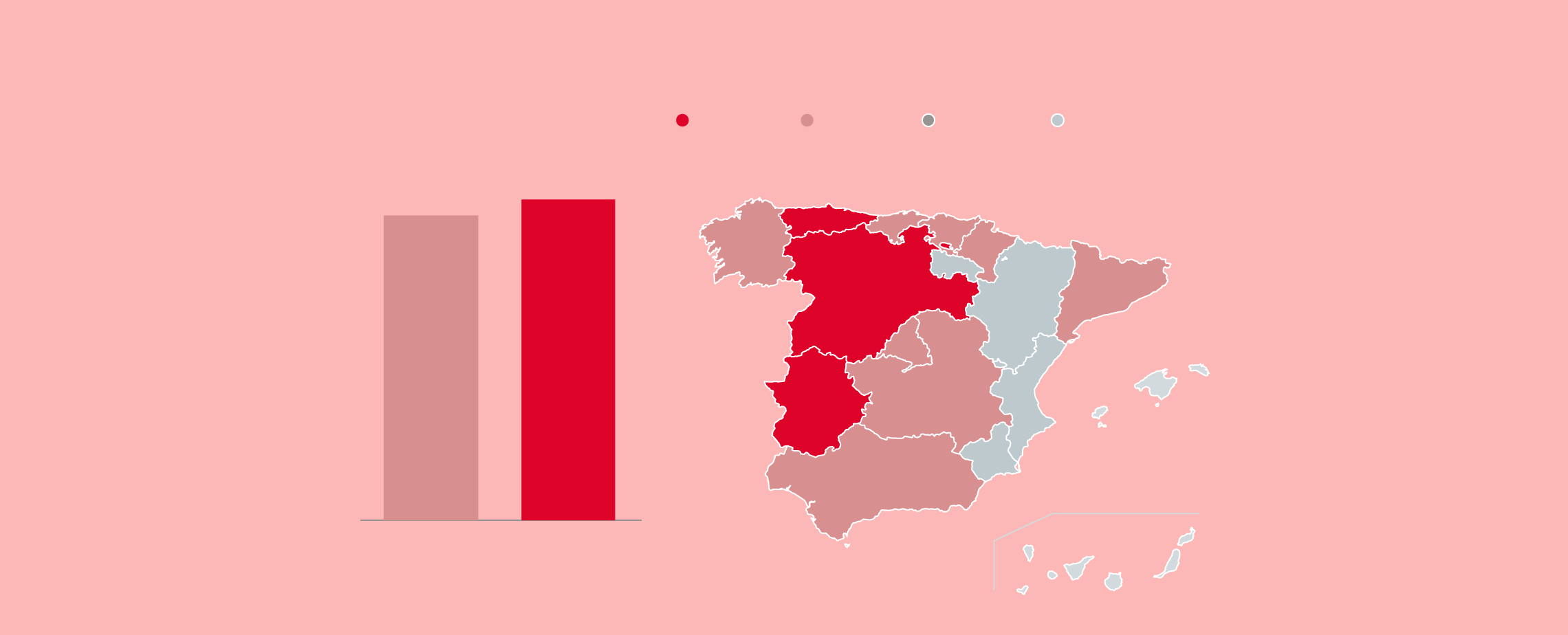
Evolution of donors
En España
Tasa por cada mil habitantes en 2021
Más de 40
De 35 a 40
De 30 a 34,9
Menos de 30
Galicia
Asturias
Cantabria
País Vasco
1.720.402
39,56
40,56
39,08
39,41
Navarra
1.632.447
38,07
Cataluña
37,02
Cast. y León
Aragón
45,55
34,38
Baleares
Madrid
29,89
36,41
C. Valenciana
Cast.-
La Mancha
Extrema-
dura
34,01
38,41
48,52
Murcia
Andalucía
32,96
35,02
Canarias
2020
2021
28,66
When fewer donations are collected than required, blood transfusion centres can call donors from their database to come forward to donate. These appeals are also made when the stock of a particular blood group is reduced.
There are also one-off campaigns such as today's World Blood Donor Day, whose motto this year is 'Donate blood, donate plasma, share life, share it often'. Plasma donation is essential as the demand for plasma has increased considerably in recent years. The proteins it contains, especially albumin and immunoglobulins, are increasingly present in drugs and therapies, so 92% of the plasma that is donated is given to pharmaceutical laboratories to be transformed and returned fractionated. The components are stored in hospital pharmacies to be administered to patients in need.
To meet this increased demand, which affects all European countries, transfusion centres are introducing apheresis donation. The donor is connected to a machine previously programmed to collect plasma or platelets. The blood passes through the machine and the machine picks up what has been programmed and returns the blood to the donor immediately.
In this way, instead of one unit of plasma, which is what is collected in a normal donation, up to four units can be collected and the donor recovers his or her levels much quicker than when donating whole blood.
This method of donation, like the traditional one, is totally safe: "Any donation goes through our centre and although scientifically it cannot be said that there is zero risk, it is very close to that value. We use molecular biology techniques, NAT techniques, capable of detecting a viral load of very few microlitres. The haemovigilance system has not detected a single transmission of disease per unit transfused in recent years," explain the transfusion centres, where different specialists analyse each donation with the latest techniques and scientific machinery.
You should know that the approximate time it takes to read this report is ten minutes, the same time it takes to make a donation that will be used to save lives. World Blood Donor Day, although it also serves to recruit new volunteers, aims to make visible the work of all those who already donate blood altruistically and regularly. Therefore, we can only add the words that are most often heard at the donation points: THANK YOU, DONORS.